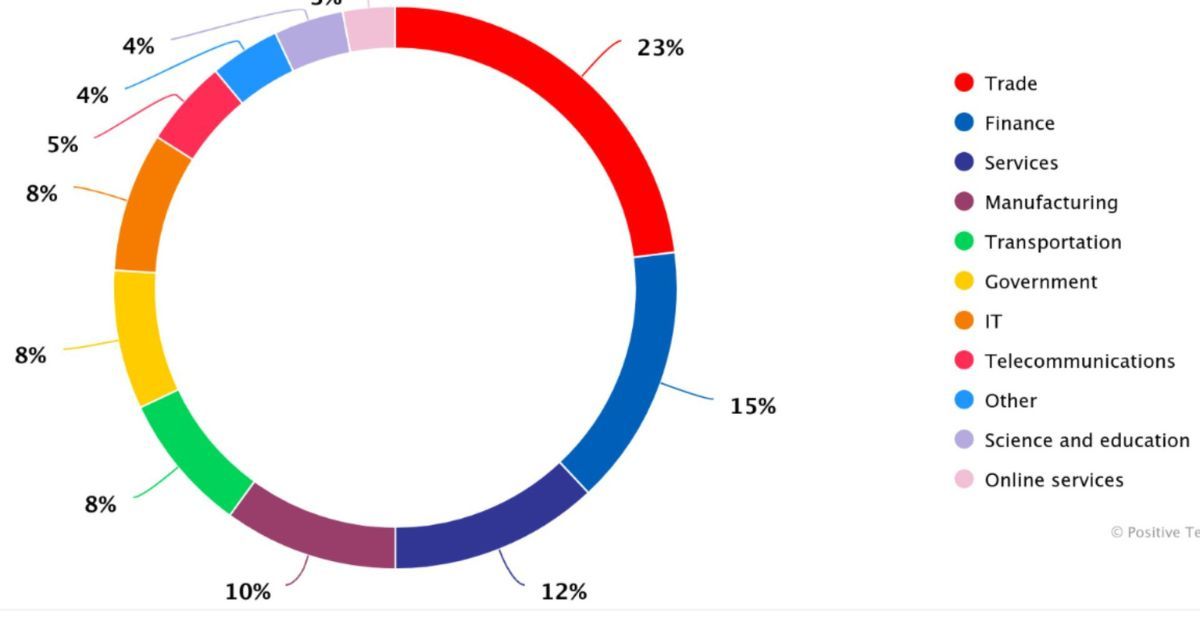
India’s rapid digital growth has made it a prime target for cyberattacks, particularly DDoS attacks. The number of such attacks has increased by 50% in 2024. Cybercriminals are primarily interested in accessing databases and critical infrastructure.
Key findings from the Positive Technologies study:
- Database Breaches: Cybercriminals are actively targeting databases containing sensitive information, including personal data and financial records.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks have become a significant threat, with hackers demanding ransom payments to unlock encrypted systems.
- Credential Theft: Stolen credentials are being sold on the dark web, enabling attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems.
To mitigate these threats, organizations in India should prioritize cybersecurity measures, including:
- Strong Network Security: Implementing robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security solutions.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary patches.
- Employee Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices to prevent social engineering attacks.
- Incident Response Planning: Having a well-defined incident response plan to minimize the impact of cyberattacks.
By adopting a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, Indian organizations can protect their critical infrastructure and sensitive data.